It’s a simple fact of life that Google has become an integral part of how we look for and receive information. The search engine has permeated nearly every walk of life – we use it to research what we’re going to eat, where we’re going to go, what is on TV or at the movies, and we even use it to cheat. Go to any pub trivia and you will see people sneaking a look at their phones to see if Google has the answer to a question that has them stumped.
Have you ever searched for something for no results to be returned, or had so many results returned that it took forever to actually find the information you were after in the first place? Have you ever wondered how you can improve your Google search skills? I’ve been using Google professionally for a long time, and I’ve put together some Google tips and tricks to share, so you can be searching like a pro in no time.
These Google search operators, tips and tricks will save you time and help you find what you want. With a little practise, your colleagues and friends will start thinking of you as a Google wizard.
Inverted Commas
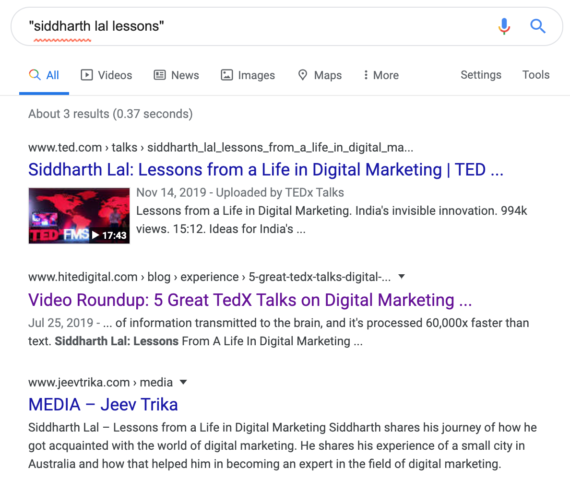
One of the most basic and powerful search tips is to use inverted commas when looking for a specific term. the quotation marks tell google to search for the whole phrase instead of the individual words, narrowing the search to very specific returns.
Example: “siddharth lal lessons”
This will search for my name and a keyword from my TED talk.
How do I use it?
Aside from ego surfing, searching with inverted commas is a great way to find very specific information, such as a person, a quote from a book, or a very specific product. Use inverted commas when you know exactly what you are looking for.
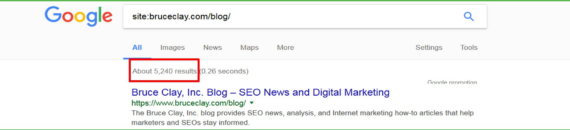
Command – Site:
This command limits the results to a specified domain. Use it to find out how many pages of your website have been indexed by Google – or if any pages are missing from the index – or if any page has been indexed multiple times thus causing duplicate content issues. This is important because if your site actually has 1000 pages but Google has only indexed 200 pages, then you will know that there is something wrong that needs to be fixed.
Example: site:yourdomain.com keyword
This will limit the results to the specified domain and a specific topic within this domain.
How do I use it?
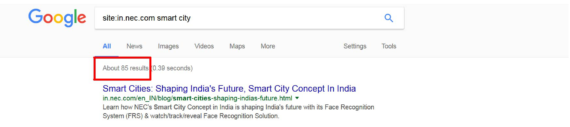
Use this command for competitive intelligence and benchmarking, such as to find out how many pages on a specific topic are present on your competitor’s site. This will help you determine how much effort needs to be put to rank for a keyword.
You can also use this command to check all the pages within your site around a specific topic. You can then strategically start linking internally.
Command – Related:
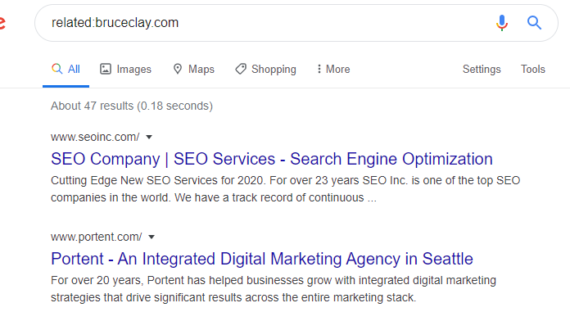
How do I use it?
This command finds sites and pages with similar keywords and themes. In the above example we have searched for bruceclay.com. Unsurprisingly given the keywords used ont eh website, Google has uncovered 47 related sites, all of which deal with SEO and search marketing.
Command – OR
The Or: command tells Google to search for one thing or the other thing, delivering results for either or both search terms rather than just results with both search terms.
Example: coronavirus OR SARS
Pro Google Tip: The pipe operator: | can be used in place of OR in a search, so instead of writing coronavirus OR SARS you can write coronavirus|SARS.
Command – Inurl:
How do I use it?
An awesome use of this command is for Guest Posting.
Example: Let’s say as part of your brand building efforts you want to increase your brand’s visibility on the Internet by finding websites that allow guest posting.
Use the “inurl” command like this:
inurl:guest post or inurl:submit guest post
Google will now show you websites that allow guest posting.
Tip > Combine two advanced search commands to further refine your search results to websites that allow guest posting on a specified topic, such as
inurl:submit guest blog intitle:marketing
Google will now show you marketing related websites that allow guest posting.
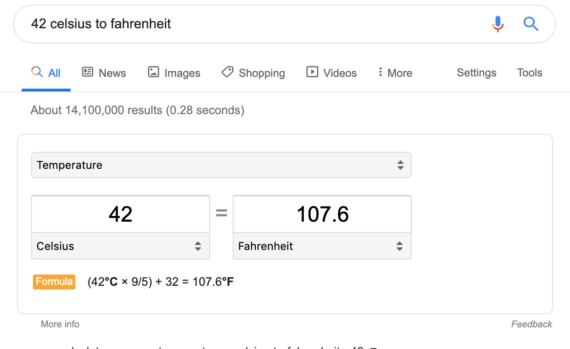
Conversions
When performing conversions from Imperial to Metric, one currency to another, Celsius to Fahrenheit and the like, most people will search for a website or utility to perform that function, but Google already has all those conversion built in. All you need to do is type the conversion you want.
Example: 42 celsius to Fahrenheit
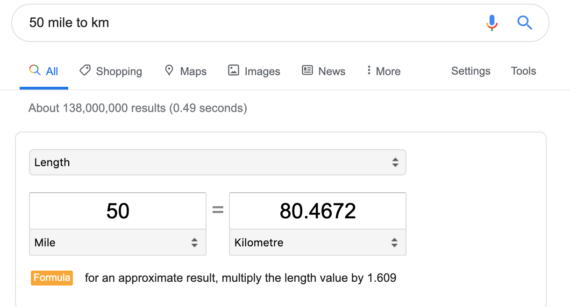
Example: 50 mile to km
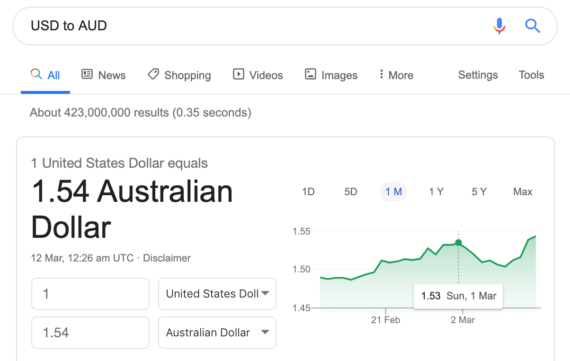
Example: USD to AUD
Command – allintitle: or intitle:
How do I use it?
You can use advanced search commands like “allintitle:” and “intitle:” to select content on topics you are writing or researching about.
You can also use this command to find your competitors.
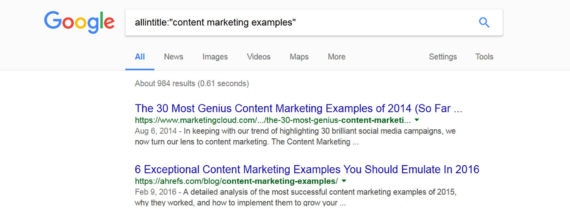
Example: Let’s say you are writing about “content marketing” and want to find all posts around this topic. Use the following search command:
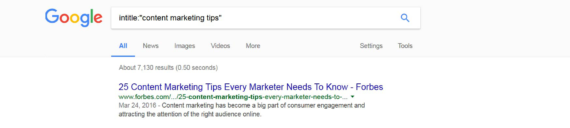
allintitle:“content marketing examples” or intitle:”content marketing tips”
Tip > Adding inverted commas to the search command will further narrow your search to only include search results that have the exact match phrase as part of the title.
Command – Cache:
Ever wondered how Google sees your web page?
Use this command to see the search engine’s cached version of your web page. This will show you what information about your webpage is in Google’s index.
Type this command directly into the search bar:
cache:coles.com.au

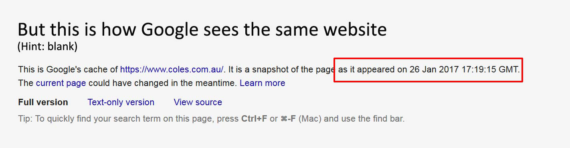
Another neat benefit of this command is that it shows you when Google checked your web page last.
a. If it has been a long time since Google last visited your web page, it might be an indication that you don’t refresh your web page with new content often enough.
b. If you have updated your content and Google has not crawled your page, then you must send a signal to Google to come and crawl your web page so that it gets updated in the Google index.
Calculator
Did you know you can perform most basic calculations right in the Google search bar? Using the following commands: +, -, /, x will add, subtract, divide or multiply your searched numbers.
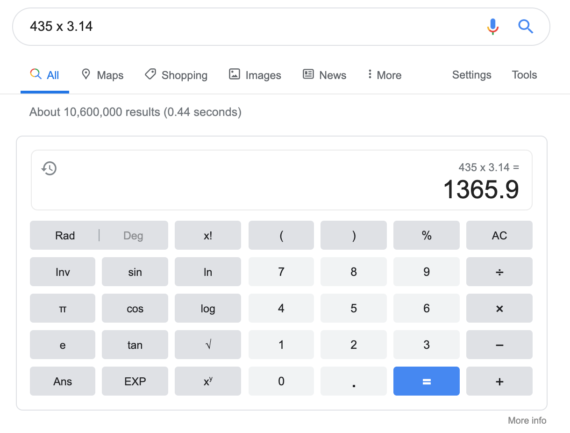
Example: 435 x 3.14

Google performs the calculation automatically for you int he search bar, but if you hit enter, it launches the Google scientific calculator for further, more in depth calculation.
Command – Filetype:
How do I use it?
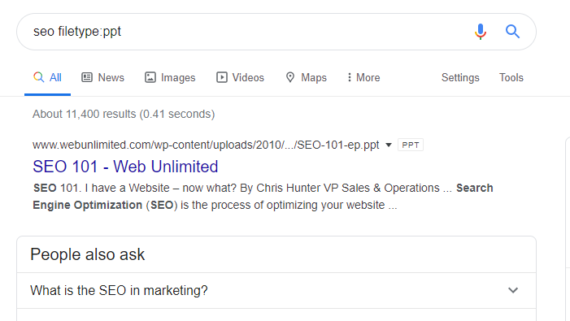
If you’re searching for a particular file type, rather than trawling through innumerable pages you can narrow your search by using the filetype: command after your search term. Say you were looking for Power Point presentations pertaining to SEO. You can type the following command into the search bar:
Seo filetype:PPT
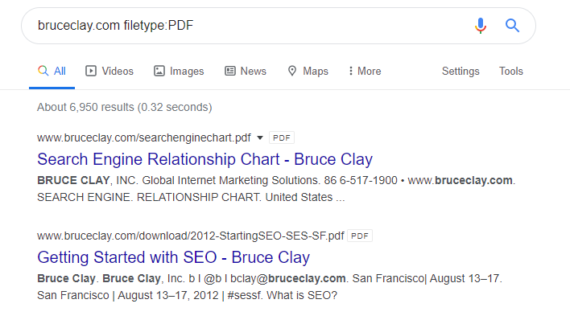
Searches can be made more specific. FOr example, if you were looking for PDFs on bruceclay.com you could search:
Bruceclay.com filetype:PDF
The following file types can be searched using the filetype: command.
- Adobe Flash (.swf)
- Adobe Portable Document Format (.pdf)
- Adobe PostScript (.ps)
- Autodesk Design Web Format (.dwf)
- Google Earth (.kml, .kmz)
- GPS eXchange Format (.gpx)
- Hancom Hanword (.hwp)
- HTML (.htm, .html, other file extensions)
- Microsoft Excel (.xls, .xlsx)
- Microsoft PowerPoint (.ppt, .pptx)
- Microsoft Word (.doc, .docx)
- OpenOffice presentation (.odp)
- OpenOffice spreadsheet (.ods)
- OpenOffice text (.odt)
- Rich Text Format (.rtf)
- Scalable Vector Graphics (.svg)
- TeX/LaTeX (.tex)
- Text (.txt, .text, other file extensions), including source code in common programming languages:
- Basic source code (.bas)
- C/C++ source code (.c, .cc, .cpp, .cxx, .h, .hpp)
- C# source code (.cs)
- Java source code (.java)
- Perl source code (.pl)
- Python source code (.py)
- Wireless Markup Language (.wml, .wap)
- XML (.xml)
Command – Inposttitle:
How do I use it?
If you’re doing blog research, you can use this command to searching for blog posts with the key words in post titles. This can be useful when looking to find a unique name for a post or to find the trending search titles for posts on a topic.E
You can also use inposttitle with other advanced search terms to further narrow the scope of the search.
Example: site:medium.com inposttitle:search marketing
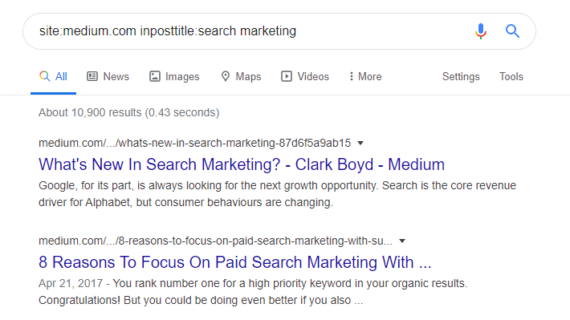
With this search we are looking for all blog posts on medium.com with search marketing in the title.
Command – intext: or allintext:
How do I use it?
The intext: command searches for a specific word somewhere on the page, whether it be the on screen text, URL or the title. You can combine this with a general search to focus your search.
Example: bruce clay intext:statistics
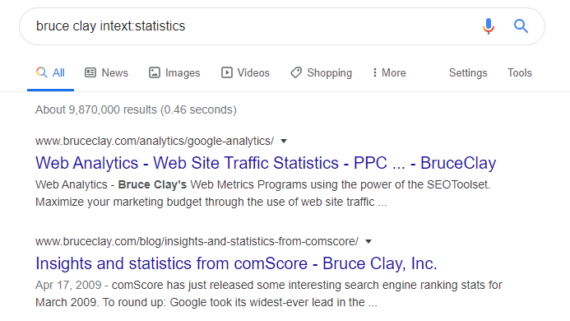
This searches for pages dealing with Bruce Clay featuring the word statistics.
The allintext command searches for a string of words on a page.
Example: allintext:bruce clay statistics
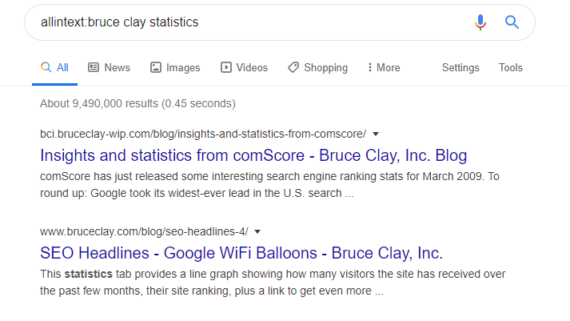
This search returns pages that contain the three searched key words.
The allintext command can also be used for a basic plagiarism or duplicated content search. By choosing an identifiable and unique phrase from your content and turning it into a specific search using inverted commas, you can discover if Google is indexing any other pages with that exact phrase on it.
Example: allintext:“Google is one of the most powerful tools available to us when it comes to marketing and brand awareness”
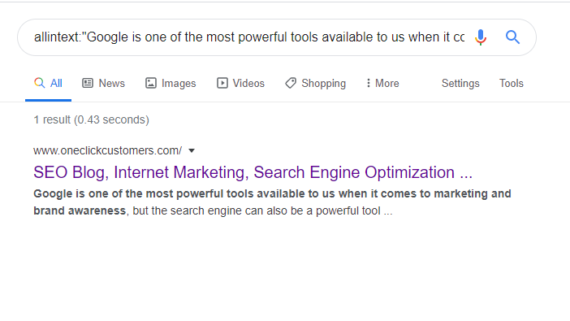
This search returns a single response. No plagiarism here.
Command + or –
Including a + or – command in your Google search will add or subtract a search term, respectively.
If you’re searching for specific information on a person, place, company or the like, then using the + command can limit searches to X search + Y parameter.
Example: Bruce Clay +Google
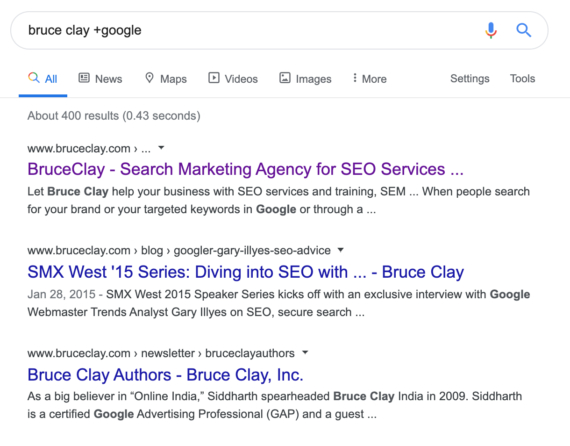
The – command tells Google to specifically search for something excluding the targeted keyword or parameter, allowing you, for example, to search for information about a company without the company’s own website appearing.
Example: Bruce Clay -bruceclay.com
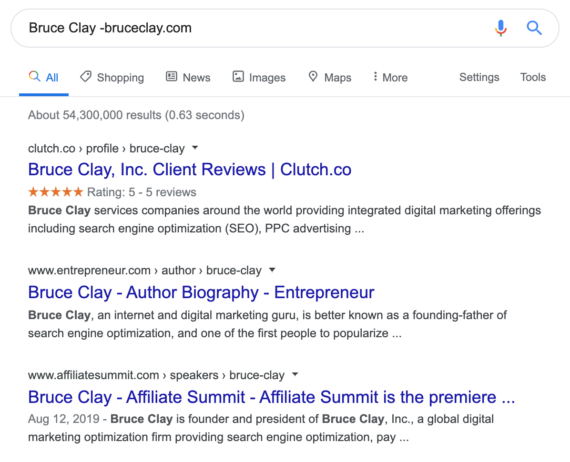
Command – Location:
How do I use it?
The location: command restricts searches to a specific geographic location, only querying sources from that specific location.
Example: Bruce Clay Location:Sydney
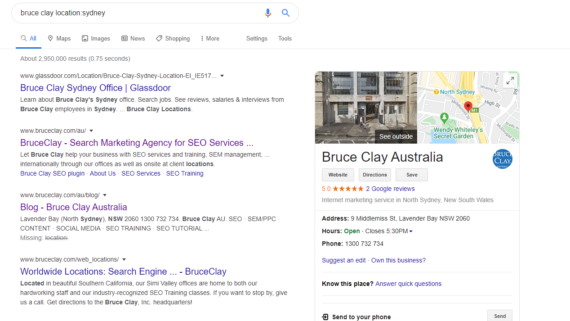
This limits searches for Bruce Clay to Australia specifically.
Limiting a search to a location can be valuable when researching how specific topics are covered in a territory, what local search terms are trending or if you’re looking to make an impact with vernacular content.
Command – Inanchor: or Allinanchor:
The inanchor and allinanchor commands restrict Google to searching for pages that contain the search term or terms in the anchor text – the visible, clickable text in a hyperlink.
How do I use it?
The inanchor command will search for a keyword in the anchor text.
Example: inanchor:SEO best practices
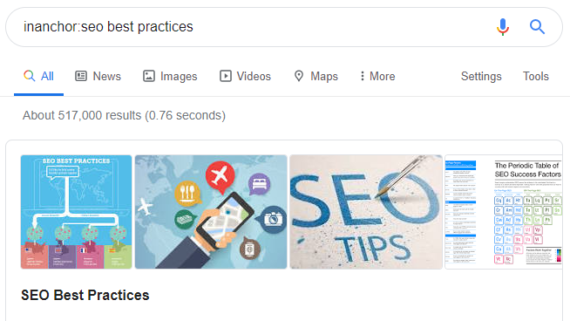
This search will look for any page with the words SEO, best or practices in the anchor text for that page. leaving us with a large number of results.
The allinanchor command further limits the search by looking for all the keywords specified in the search in the anchor text.
Example: allinanchor:seo best practices
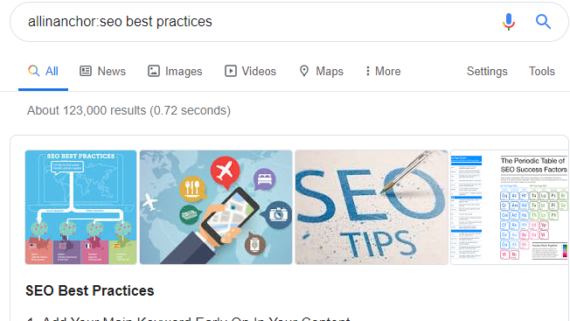
This search returns far fewer results as we require every page returned to contain the three search terms in the anchor text.
The search can be further refined by placing the search term in inverted commas, making google search for that exact phrase.
Example: allinanchor:”seo best practices”
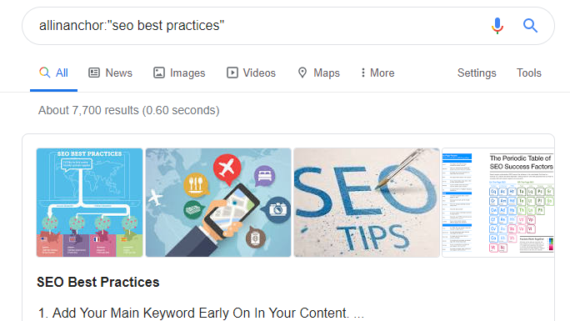
The inanchor and allinanchor commands are useful for identifying guest posting and potential outreach opportunities.
Example: “guest post” inanchor:contact
This search looks for the term guest post and anchor text containing contact, identifying guest posting contact pages.
